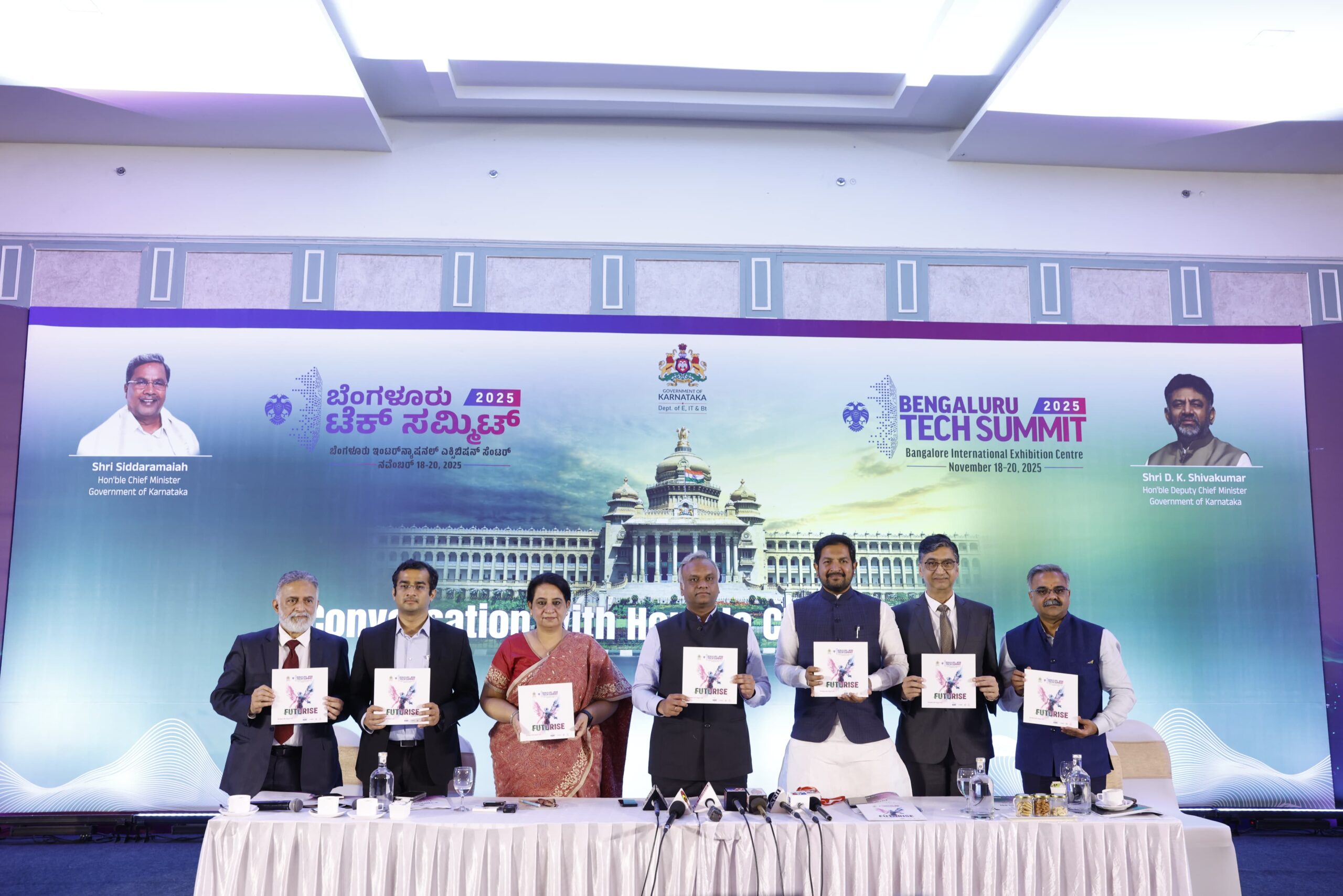
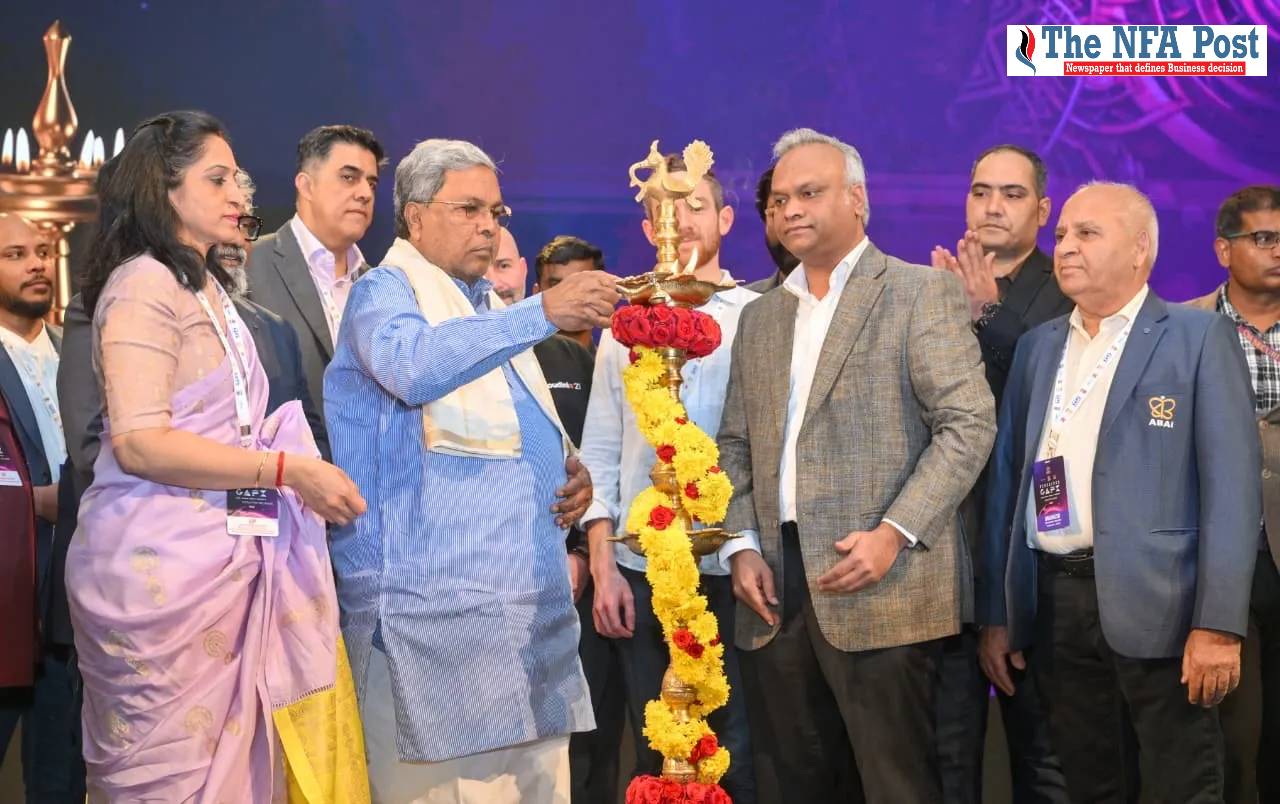
“We are not just embracing emerging technologies; we are defining them,” says CM Siddaramaiah as Karnataka unveils bold new vision for Asia’s largest tech event
Bengaluru, NFAPost: Bengaluru is set to raise the bar for global technology gatherings as the 28th edition of the Bengaluru Tech Summit (BTS) gears up for its biggest-ever outing from November 18–20, 2025, under the theme ‘Futurise’. Announced today by Shri Priyank Kharge, Minister for IT & BT and RDPR, Government of Karnataka, BTS 2025 will make its debut at the Bangalore International Exhibition Centre (BIEC) — a purpose-built, eco-conscious venue equipped with expansive halls, world-class conference facilities, and metro connectivity.
The shift to BIEC marks a significant scale-up for Asia’s largest tech event, with over 1,00,000 attendees expected, including 20,000+ startup founders, 1,000+ investors, 600+ speakers, and 1,200+ exhibitors from 60+ countries. The summit will host 10 conference tracks, ranging from IT & DeepTech, Digital Health, and Electro-Semicon to bold new additions like AI Universe, Finverse, Defence & Spacetech, and My Planet My Future.
“With 44% of India’s software exports, over 18,300 startups, 875+ Global Capability Centres, and nearly half of the nation’s AI talent, we are not just embracing emerging technologies; we are defining them,” declared Chief Minister Shri Siddaramaiah.
“Our mission is to make Karnataka the place the world looks to for leadership in innovation, talent, and technology.”
The event will feature Future Makers Conclave, drawing over 20,000 startup ecosystem members; an expanded Startup Springboard for investor pitching, mentoring clinics, and global market access; and minister-led country delegations under the Global Innovation Alliance to foster cross-border collaboration.
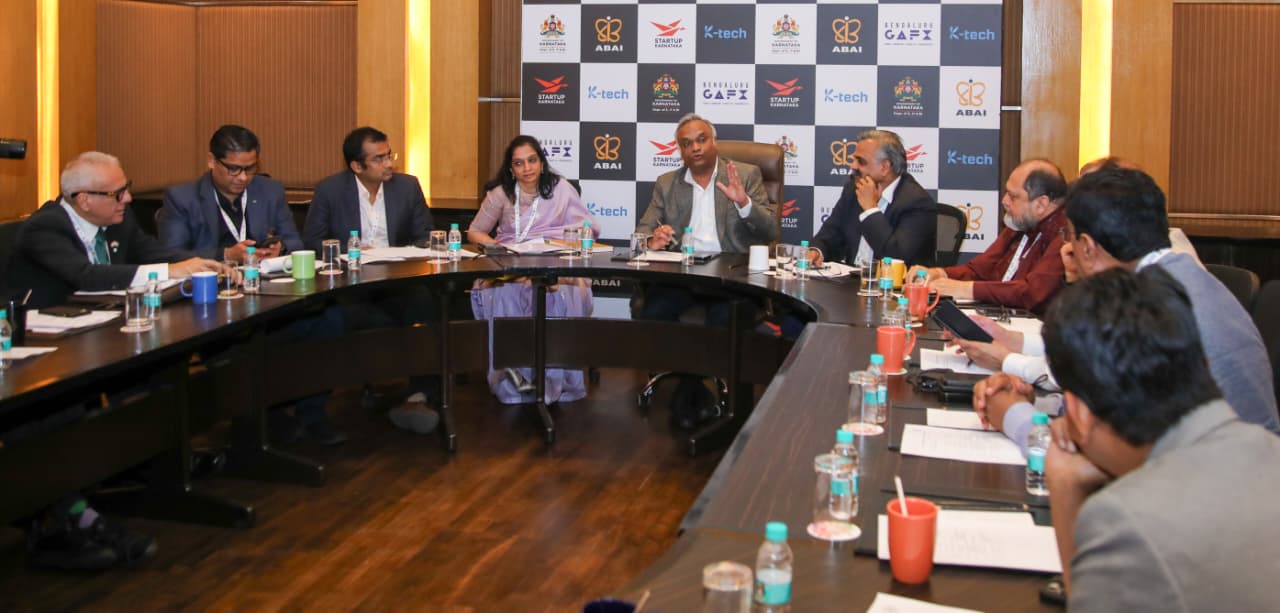
At a high-powered CEO Breakfast Meet earlier today, attended by 200 industry leaders, discussions centred on policy, infrastructure, and innovation strategies. Deputy Chief Minister Shri D.K. Shivakumar emphasized the government’s focus on inclusive growth and livability, stating:
“Beyond policies, our focus is on trust, collaboration and real outcomes… positioning Karnataka as the global hub for talent, investment and innovation.”
The summit announcement also saw the unveiling of the Karnataka Tech Landscape Progress Report and the launch of KATALYST, an Ease of Doing Business cell dedicated to supporting Global Capability Centres in line with the GCC Policy 2024–2029.
Industry stalwarts including Kris Gopalakrishnan, Dr. Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw, Prashanth Prakash, and Dr. A.S. Kiran Kumar shared insights on sectoral opportunities and strategic growth paths, reinforcing Karnataka’s position as a frontrunner in tech-led transformation.
As BTS 2025 approaches, the message from Karnataka’s leadership is clear: Bengaluru is not just hosting a summit — it is setting the agenda for the future of global technology.