Bengaluru, NFAPost: In a significant stride for India’s lunar exploration efforts, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced on Sunday that it has successfully executed the orbit reduction manoeuvre for Chandrayaan-3, the nation’s third moon mission. This achievement comes just a day after the spacecraft was inserted into the lunar orbit.
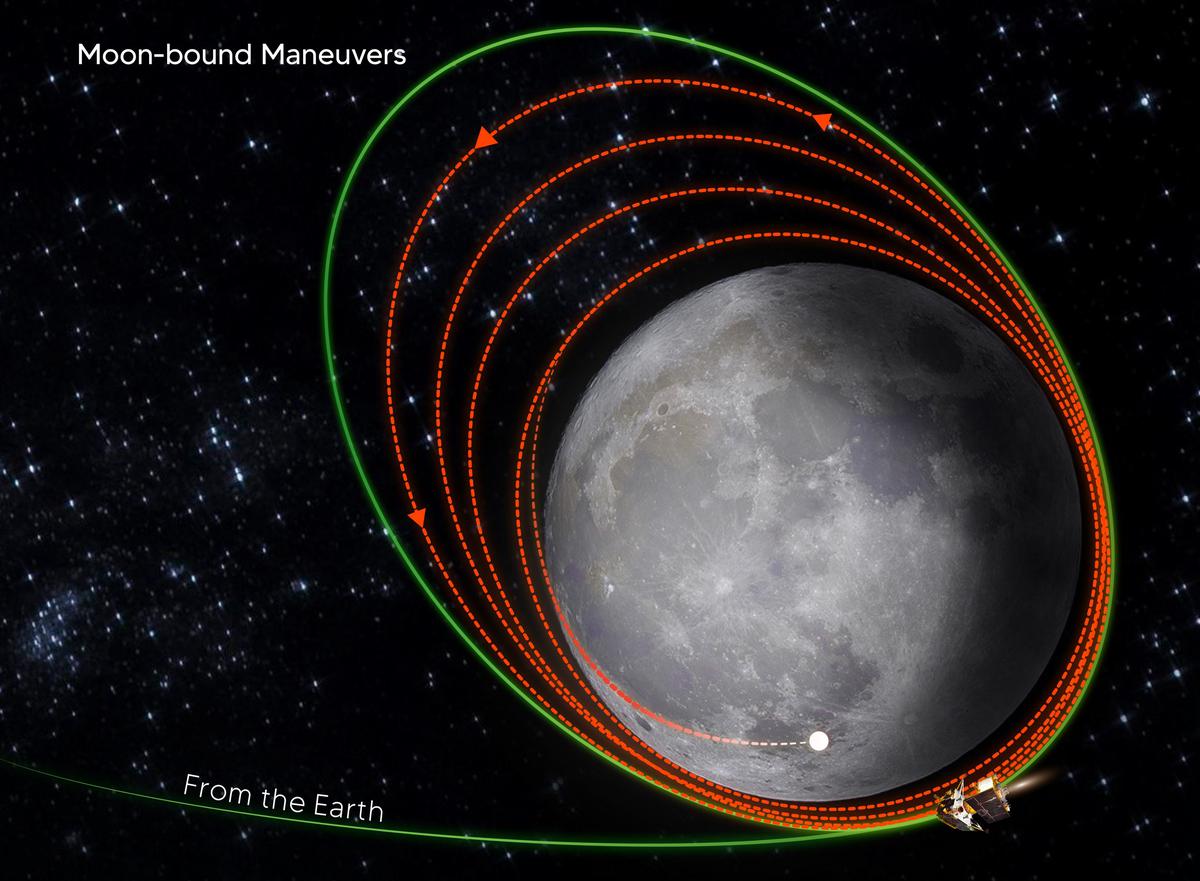
The carefully planned retrofitting of the spacecraft’s engines has brought it closer to the moon’s surface, positioning it at an orbit of 170 km x 4,313 km. ISRO revealed that the next crucial operation is scheduled for August 9, 2023, between 1300 and 1400 hrs IST, during which the orbit will be further diminished.
The upcoming days will witness three more lunar-bound manoeuvres until August 17. Following these adjustments, the landing module, comprising both the lander and rover, will disengage from the propulsion module. Subsequently, de-orbiting manoeuvres will be carried out on the lander, paving the way for its final descent onto the moon’s surface. The culmination of these efforts will be an attempted soft landing on August 23, as per ISRO’s plans.
Since its launch on July 14, ISRO has conducted over five precise manoeuvres, incrementally shifting the Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft to progressively distant orbits from Earth. This mission is conceived as a follow-on from Chandrayaan-2, aiming to showcase India’s prowess in safely landing and roving on the lunar terrain.
Chandrayaan-3 comprises three core components: an indigenous propulsion module, a lander module, and a rover. These components are tasked with demonstrating the novel technologies essential for interplanetary missions. The propulsion module plays a crucial role in ferrying the lander and rover configuration up to a distance of 100 km from the lunar orbit. Notably, it is equipped with the Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) payload, designed to conduct spectral and polarimetric assessments of Earth from the vantage point of lunar orbit.
The lander module boasts the capability to execute a gentle landing at a designated lunar site, facilitating the deployment of the rover. The rover, in turn, is primed to conduct in-situ chemical analysis of the lunar surface during its mobility. Both the lander and the rover are outfitted with scientific instruments aimed at carrying out an array of experiments on the moon’s terrain. This mission underscores India’s determination to advance its scientific footprint in space exploration and technology innovation.