What is Google Bard
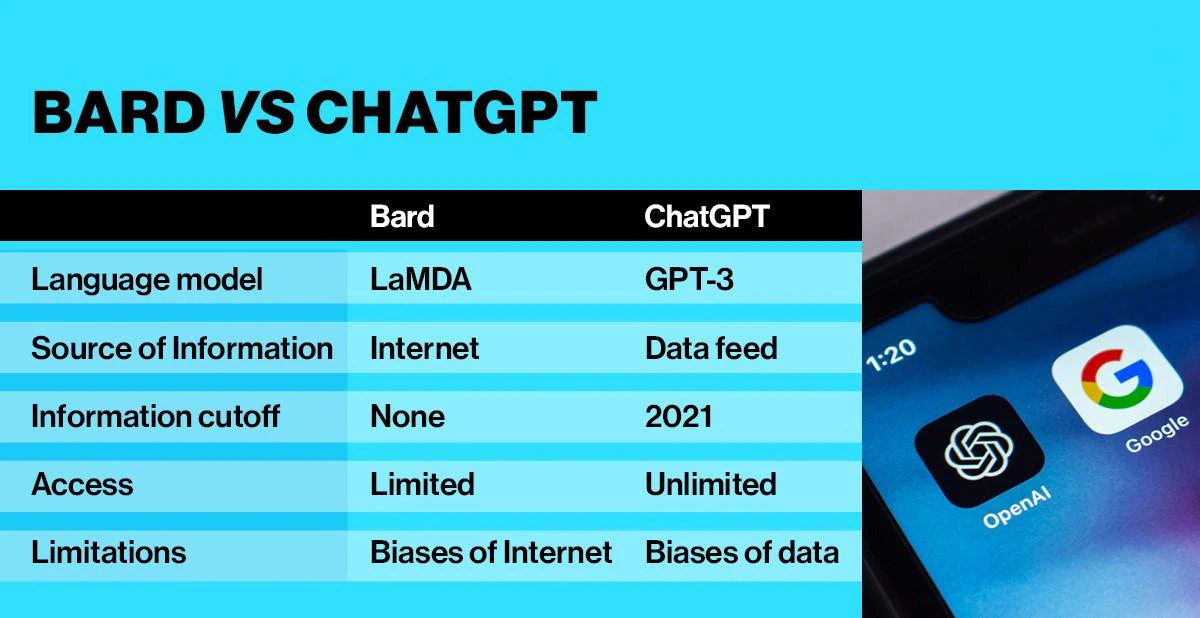
Bard is a chat service developed by Google that utilizes artificial intelligence to engage in conversations with users. Unlike ChatGPT, which relies on its internal knowledge, Bard draws information from the internet to provide relevant responses.
- Bard is based on the Language Model for Dialogue Application (LaMDA), Google’s own conversational AI chatbot.
- It will give in-depth, conversational and essay-style answers just like ChatGPT does right now.
- However, the model is currently a “lightweight” version of LaMDA, and the one being “requires significantly less computing power, enabling it to scale to more users.
How does Google Bard work

- It is built on Transformer technology, which is also the backbone of ChatGPT and other AI bots.
- Transformer technology was pioneered by Google and made open source in 2017.
- Transformer technology is a Neural Network Architecture, which is capable of making predictions based on inputs and is primarily used in natural language processing and computer vision technology.
- The architecture determines how the network processes information and influences its accuracy and efficiency in solving a particular problem. Common architectures include feedforward networks, recurrent networks, and convolutional neural networks.
Is Bard Better than ChatGPT

- Currently, Bard looks like a limited rollout and it is hard to say whether it can answer more questions than ChatGPT.
- Google has also not made clear the amount of knowledge that Bard possesses. For instance, with ChatGPT, we know its knowledge is limited to events till 2021.
What are the Limitations of such AI Chatbots?
- They sometimes write plausible-sounding but incorrect or nonsensical answers.
- The models are often excessively verbose and overuse certain phrases.
- While efforts have been made to make these models refuse inappropriate requests, they will sometimes respond to harmful instructions or exhibit biased behaviour.
- Running these models requires significant computing power (ChatGPT is powered by Microsoft’s Azure Cloud services).
- This explains why the service often runs into errors at times because too many people are accessing it.





